 By: OpenKit on Jan 16 2025
By: OpenKit on Jan 16 2025 What Are AI Agents? The Complete Guide to Intelligent Automation
A comprehensive guide to AI agents and intelligent systems. Understand their types, capabilities, and real-world applications in business automation and decision-making.
Introduction
At OpenKit, we see the transformative impact of AI agents daily through our work across education, legal analysis, and environmental monitoring. Through projects like our CodeKit™ AI tutor and BAiSICS legal platform, we’ve witnessed these autonomous systems evolve from simple automation tools into sophisticated problem-solving partners.
But what sets AI agents apart in today’s technological landscape? Unlike conventional software that follows rigid instructions, AI agents operate with remarkable independence - they observe their environment, process information, make decisions, and take action to achieve specific goals. Our experience developing solutions like Air Aware demonstrates how these systems can analyse complex patterns, make nuanced decisions, and adapt to new situations with minimal human oversight.
The impact extends far beyond basic task automation. From guiding students through complex programming concepts to analysing legal documents in seconds, AI agents are reshaping how organisations operate and innovate. For business leaders and technologists alike, understanding these systems has become crucial as they increasingly drive efficiency across sectors.
This comprehensive guide draws from our practical experience implementing AI agents across diverse industries. We’ll explore their fundamental principles, examine how they work, and investigate their practical applications through real-world examples. Whether you’re considering implementing AI agents in your organisation or seeking to deepen your understanding of this transformative technology, this article will provide you with actionable insights and practical knowledge.
Let’s begin by examining the core concepts that make AI agents uniquely powerful in today’s technological landscape.
Understanding AI Agents: Core Concepts and Principles
Through implementing AI solutions across diverse sectors, we’ve identified three essential characteristics that define successful AI agents. These traits distinguish them from conventional automation and enable their unique problem-solving capabilities.
Core Characteristics
| Characteristic | Definition | Examples from Our Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Independent operation without constant oversight | Our CodeKit™ platform adapts teaching methods based on student performance, requiring no manual adjustments |
| Rationality | Data-driven decision making for optimal outcomes | BAiSICS evaluates document context and importance to prioritise critical legal information |
| Goal-Oriented Behavior | Persistent work toward defined objectives | Air Aware continuously adjusts monitoring strategies to maintain accurate pollution tracking |
These characteristics work together to create systems that handle complex tasks with minimal human intervention. In our legal document analysis platform, for instance, the agent’s autonomy allows it to process thousands of pages independently, while its rational decision-making helps identify crucial legal points, all directed toward the goal of comprehensive document analysis.
Beyond Traditional AI
What truly sets AI agents apart from conventional AI systems is their ability to:
- Initiate actions independently based on environmental changes
- Adapt strategies based on new information
- Maintain progress toward goals despite obstacles
- Learn from experience to improve future performance
For example, while a standard document processing system might flag keywords, our legal AI agent:
- Identifies contextual relationships between documents
- Adapts its analysis based on document type and purpose
- Maintains accuracy across varying document formats
- Improves its understanding of legal terminology over time
Through implementing these systems across different industries, we’ve learned that successful AI agents require more than just sophisticated algorithms - they need carefully designed frameworks for perceiving their environment, making decisions, and taking action. Let’s examine these components in detail.
Distinguishing AI Agents from Other AI Systems
While many AI technologies excel at specific tasks, AI agents combine multiple capabilities to create truly autonomous systems. Consider the differences:
| Aspect | Traditional AI Systems | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | ❌ Single-purpose only | ✅ Multi-purpose capability |
| Operation | ❌ Requires explicit instructions | ✅ Autonomous decision-making |
| Adaptability | ❌ Limited adaptability | ✅ Adaptive learning |
| Flexibility | ❌ Strict parameters | ✅ Flexible within defined goals |
For instance, whilst a traditional chatbot follows predetermined scripts, an AI agent functioning as a customer service representative can:
- Understand context and intent
- Access relevant information independently
- Make decisions about how to resolve issues
- Learn from each interaction to improve future responses
AI agents often leverage machine learning capabilities, but they’re not synonymous with machine learning systems. Rather, machine learning serves as one of many tools that agents can use to improve their performance and decision-making capabilities.
Environmental Interaction
AI agents interact with their environment through three primary mechanisms:
- Sensors (for gathering information)
- Processors (for decision-making)
- Actuators (for taking action)
Understanding these fundamental concepts provides the foundation for exploring how AI agents are constructed and how they function in practice. Let’s examine the specific components that enable these capabilities in more detail.
Types of AI Agents
From simple rule-based systems to sophisticated learning agents, the evolution of AI agents reflects the advancement of artificial intelligence itself.
Simple Reflex Agents
Condition-Action Rules
Direct mapping between perception and action
Immediate Response
Acts purely on current input
No Memory
Doesn’t maintain internal state
The most basic form of AI agents, simple reflex agents operate on a fundamental ‘condition-action’ rule set. These agents function using direct stimulus-response mechanisms, reacting only to their current perceptions without maintaining any internal state or memory of past actions.
Practical Applications
Basic chatbots
Automated email responders
Temperature controls
Simple process automation
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Internal Model
Maintains world representation
State Tracking
Monitors environmental changes
Informed Decisions
Uses history and context
Model-based reflex agents represent a significant advancement over simple reflex agents. They maintain an internal model of their environment, allowing them to make more informed decisions based on both current perceptions and historical context.
Key Applications
Automated trading systems
Smart home controllers
Process monitoring
Environmental control systems
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-Oriented
Explicit objective targeting
Strategic Planning
Maps path to objectives
Outcome Evaluation
Assesses goal achievement
Goal-based agents represent a significant advancement in autonomous decision-making. These agents evaluate actions based on how they contribute to achieving specific goals, rather than just following predetermined rules. They can consider multiple possible paths to reach their objectives and choose the most effective approach.
Primary Applications
Project management systems
Automated planning tools
Logistics optimisation
Strategic gaming AI
Utility-Based Agents
Value Optimisation
Maximises utility outcomes
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Evaluates trade-offs
Preference-Based
Considers desired outcomes
Utility-based agents add another layer of sophistication by evaluating multiple possible outcomes against a utility function. These agents don’t just achieve goals—they optimise for the best possible outcome based on defined preferences and values. They can handle complex scenarios with multiple competing objectives.
Key Applications
Financial planning systems
Resource allocation
Investment optimisation
Decision support systems
Learning Agents
Adaptive Learning
Improves from experience
Performance Evolution
Continuous improvement
Dynamic Adaptation
Evolves with environment
Learning agents represent the most advanced single-agent category, capable of continuous improvement through experience. They combine the capabilities of other agent types while adding robust learning mechanisms. These agents can adapt to new situations and improve their performance over time through various learning algorithms.
Advanced Applications
Advanced recommendation systems
Autonomous vehicles
Adaptive security systems
Personalised learning platforms
Multi-Agent Systems
Collaborative Intelligence
Agent cooperation
Distributed Processing
Parallel problem-solving
Emergent Behavior
Complex system interactions
Multi-agent systems represent the pinnacle of AI agent technology, combining multiple agent types into collaborative networks. These systems leverage the strengths of different agent types while mitigating their individual limitations. Through agent cooperation and coordination, they can tackle complex problems that would be impossible for single agents to solve.
Complex Applications
Smart city systems
Supply chain optimisation
Distributed computing networks
Emergency response coordination
How AI Agents Work
The working mechanisms of AI agents involve distinct phases of perception, analysis, and action. Like a human decision-maker, an AI agent processes information through a sophisticated cycle of understanding, reasoning, and response. This process enables agents to handle complex tasks autonomously while adapting to changing circumstances.
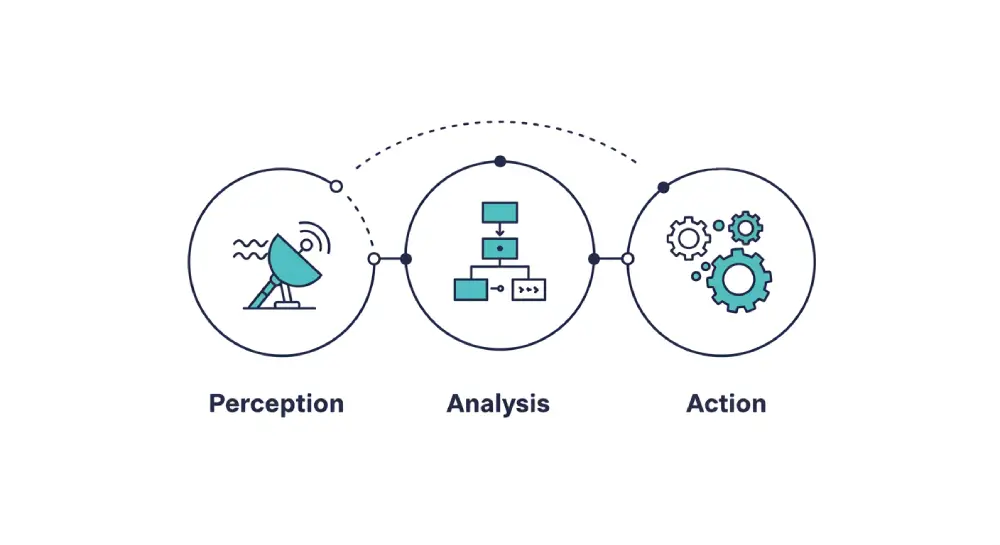
The Perception Phase
AI agents begin their operation cycle by gathering data through various interfaces. This critical first step involves continuous monitoring of designated data sources, real-time signal processing, and pattern detection in incoming data. The agent processes raw information through sophisticated filtering mechanisms, normalising data formats and standardising inputs for effective analysis.
During this phase, agents employ multiple data collection methods, from direct sensor readings to API integrations. This multi-modal approach ensures comprehensive environmental awareness, allowing the agent to build a complete picture of its operational context. The quality of this initial data gathering significantly impacts the effectiveness of subsequent decision-making processes.
The Analysis Phase
In the analysis phase, AI agents process collected data through sophisticated interpretation mechanisms. This involves context building, where historical data is integrated with current information to form a comprehensive understanding of the situation. The agent applies various analytical frameworks to identify patterns, assess relationships between different data points, and generate meaningful insights.
The decision framework application during this phase is particularly crucial. Agents evaluate potential actions against their programmed objectives, considering both immediate outcomes and longer-term implications. This process involves careful resource assessment, where the agent evaluates available tools, time constraints, and potential risks associated with different courses of action.
The Action Phase
The final phase involves executing chosen actions based on the analysis results. Actions can range from generating responses in a conversation to controlling physical systems in the real world. The execution process includes careful monitoring of action outcomes, allowing the agent to adjust its approach in real-time if needed.
Throughout this phase, agents maintain feedback loops that help them understand the effectiveness of their actions. This continuous monitoring enables learning and adaptation, helping the agent improve its performance over time. The action phase also includes mechanisms for handling unexpected situations or errors, ensuring robust and reliable operation even in challenging circumstances.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Beyond these core phases, AI agents engage in continuous learning and adaptation. This ongoing process involves analysing the outcomes of past actions, identifying patterns in successful and unsuccessful operations, and adjusting internal models and decision-making processes accordingly. This learning capability ensures that agents become more effective over time, building on their experiences to handle increasingly complex situations with greater sophistication.
The integration of these phases – perception, analysis, action, and learning – creates a dynamic system capable of handling complex tasks with increasing competence. As AI technology continues to evolve, these mechanisms become more sophisticated, enabling agents to tackle increasingly challenging problems while maintaining reliability and effectiveness.
Applications and Use Cases
The theoretical potential of AI agents becomes tangible when examining real-world implementations. Let’s explore how these intelligent systems are transforming various sectors.
Education and Learning
AI agents are revolutionising educational experiences through personalised tutoring and adaptive learning systems, transforming how students engage with complex subjects.
CodeKit™
Real-time contextual guidance and adaptive programming education
Legal Document Analysis
In the legal sector, AI agents are transforming document processing workflows, bringing unprecedented efficiency and accuracy to legal document analysis.
BAiSICS
High-precision legal document processing and analysis platform
Environmental Monitoring and Public Health
AI agents are increasingly crucial in environmental monitoring and public health awareness, providing real-time insights and community engagement.
Air Aware
Real-time environmental monitoring and community health platform
Enterprise Integration
Customer Service
Providing 24/7 customer support through intelligent query routing and contextual response generation. Systems continuously learn from interactions to improve service quality.
Process Automation
Optimising workflows through intelligent document processing and decision support systems, ensuring consistent quality control across operations.
Data Analysis
Real-time processing and pattern recognition enabling predictive analytics and actionable insights generation for informed decision-making.
Emerging Applications
The potential of AI agents continues to expand into new territories. Current emerging applications include multi-agent collaborative systems, autonomous decision-making platforms, cross-domain intelligence integration, and advanced learning systems. These developments promise to further revolutionise how we interact with and benefit from artificial intelligence.
Benefits and Challenges
The integration of AI agents into organisational processes represents both tremendous opportunity and significant challenge. Understanding both aspects is crucial for successful implementation and realistic expectation setting.
Transformative Benefits
The transformative potential of AI agents manifests across multiple dimensions. In education, we’ve observed how intelligent tutoring systems fundamentally alter the learning experience. Students receiving personalised guidance show markedly improved engagement and comprehension. The AI agent doesn’t simply provide answers – it adapts its teaching approach based on individual learning patterns.
In the legal sector, the impact on efficiency proves equally profound. Document analysis that once consumed hours of professional time now completes in minutes, while maintaining exacting standards of accuracy. More importantly, the consistency of analysis improves as AI agents apply uniform scrutiny across vast document collections.
Perhaps most significantly, AI agents demonstrate remarkable capability for continuous improvement. Unlike traditional software systems, they learn from each interaction, gradually enhancing their effectiveness. This adaptive quality proves particularly valuable in dynamic environments where requirements frequently evolve.
Operational Advantages
The operational advantages manifest in several key areas. Response times to customer queries reduce dramatically, often from hours to seconds. Process consistency improves as AI agents apply standardised approaches across operations. Resource utilisation becomes more efficient as routine tasks shift to automated handling.
Yet the most profound benefit may be in decision support. AI agents process vast amounts of data to surface insights that might otherwise remain hidden. In environmental monitoring, for instance, they identify subtle patterns in air quality data that inform public health strategies.
Significant Challenges
However, implementing AI agents presents significant challenges that require careful consideration. Technical complexity remains a primary concern. Developing effective AI agents demands sophisticated understanding of both artificial intelligence and specific domain requirements. Our experience with BAiSICS demonstrates the importance of extensive testing and refinement to achieve reliable performance.
Data quality and availability present another crucial challenge. AI agents require substantial, high-quality data for training and operation. Organisations often underestimate the effort required to prepare and maintain appropriate data resources.
Integration with existing systems and processes demands careful planning. AI agents must seamlessly connect with established workflows while maintaining security and compliance requirements. This often requires significant infrastructure adaptation.
Future Outlook: Evolution and Impact
The future of AI agents represents a fascinating convergence of technological advancement and practical application. As we’ve observed through our work developing intelligent tutoring systems, legal analysis platforms, and environmental monitoring solutions, these systems are evolving in increasingly sophisticated ways.
Multi-Agent Collaboration
One clear direction of evolution emerges in the realm of multi-agent collaboration. Where individual AI agents once operated in isolation, we’re witnessing the emergence of interconnected systems that share knowledge and capabilities. In our legal document analysis platform, for instance, specialised agents now work in concert - some focusing on document processing while others handle pattern recognition and analysis.
Human-AI Interaction
The relationship between humans and AI agents continues to transform. Through our experience with CodeKit’s educational platform, we’ve observed how AI agents increasingly adapt to individual human working and learning styles. This evolution suggests a future where AI agents function less as tools and more as collaborative partners, understanding and adapting to human needs while maintaining clear ethical boundaries.
Technological Advancement
Advancing capabilities in natural language processing and understanding enable increasingly nuanced interaction between humans and AI agents. Yet perhaps more significant is the evolution in learning capabilities. Modern AI agents demonstrate remarkable ability to learn from experience, refining their responses and adapting their strategies based on outcomes.
Organisational Impact
Organisations implementing AI agents today are pioneering tomorrow’s operational models. We’re witnessing the emergence of hybrid workflows where human expertise and AI capabilities complement each other in increasingly sophisticated ways. Through Air Aware’s deployment, we’ve seen how AI agents can enhance human decision-making while learning from human expertise.
Sector-Specific Evolution
Different sectors will likely evolve distinct applications of AI agent technology. In education, we anticipate increasingly sophisticated personalised learning experiences. Legal and financial sectors may see enhanced analytical capabilities, while environmental monitoring could benefit from more advanced predictive modelling.
Societal Implications
The societal impact of advancing AI agent capabilities warrants careful consideration. While these systems offer tremendous potential for enhancing human capabilities and solving complex problems, their development must be guided by clear ethical principles and consideration of human values.
Conclusion: Understanding AI Agents
As we’ve explored the intricate world of AI agents, from their fundamental principles to future possibilities, one truth becomes increasingly clear: we stand at the threshold of a transformative era in human-machine collaboration.
Through our journey developing solutions like CodeKit, BAiSICS, and Air Aware, we’ve witnessed firsthand how AI agents can enhance human capabilities across diverse domains. Yet understanding these systems is merely the first step toward effective implementation.
The potential of AI agents manifests most powerfully when aligned with clear organisational objectives. Whether enhancing educational experiences, streamlining legal processes, or monitoring environmental conditions, success stems from thoughtful application rather than mere technological adoption.
The relationship between humans and AI agents continues to evolve, shaped by advancing technology and growing understanding of effective collaboration. As these systems become more sophisticated, maintaining focus on human values and ethical considerations becomes increasingly important.
For organisations considering AI agent implementation, the journey begins with thorough understanding followed by careful planning. In our upcoming article on AI agent implementation, we’ll explore practical steps, technical considerations, and best practices drawn from real-world deployments.
The future of AI agents holds tremendous promise for enhancing human capabilities and solving complex challenges. Yet realising this potential requires balanced approach - embracing innovation while maintaining clear focus on human needs and ethical considerations.
Stay tuned for our next article in this series, where we’ll provide a comprehensive guide to implementing AI agents in your organisation, including technical requirements, best practices, and real-world case studies from our experience.
Ready to explore how AI agents can transform your business? OpenKit specialises in developing custom AI agent solutions that drive efficiency and innovation.
Discover Our AI Services | Contact Us to Discuss Your Project






